During this post we will discuss multiple scenario on Clustering Tables. We will be analyzing and implementing the following scenarios in this post.
- Non Cluster to Cluster table : Create Clustering on Normal table and see the partitions pruning.
- CLONE Cluster table: CLONE the above Clustered table and analyze the Clustering.
- COPY Cluster table: COPY the same Clustered table and analyze the changes.
Case 1: Create a CUSTOMER table and run the query without any Clustering enabled on the table
CREATE OR REPLACE TRANSIENT TABLE CUSTOMER
AS SELECT * FROM "SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA"."TPCH_SF1000"."CUSTOMER"
=====================================================================
select * from CUSTOMER where C_MKTSEGMENT = 'MACHINERY'
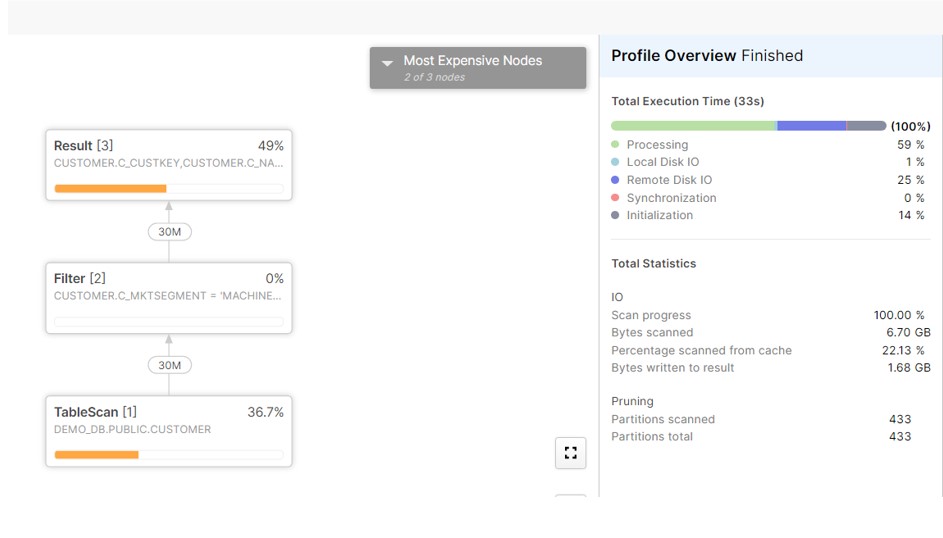
Query Profile : It has scanned all partitions from the table
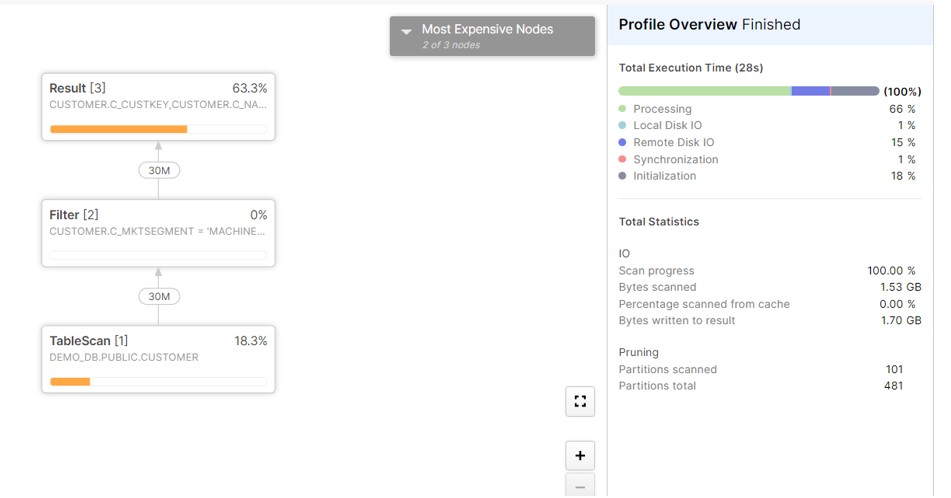
Now Apply the cluster on the Table and verify the Query Profile:
ALTER TABLE CUSTOMER CLUSTER BY (C_MKTSEGMENT);
SELECT * FROM TABLE(information_schema.AUTOMATIC_CLUSTERING_HISTORY());
select * from CUSTOMER where C_MKTSEGMENT = 'MACHINERY'
As we can see, after the cluster it has pruned the partition and scanned only 101 out of 481 partitions.
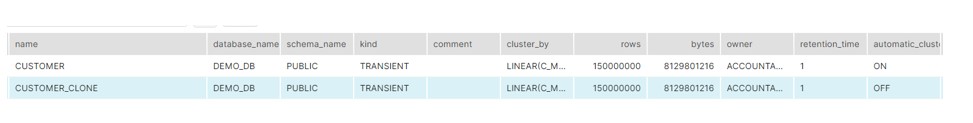
Case 2: Create the CLONE of Clustered CUSTOMER table
CREATE OR REPLACE TRANSIENT TABLE CUSTOMER_CLONE CLONE CUSTOMER;
We can see in below screenshot, that CLONE table “CUSTOMER_CLONE” is clustered but AUTOMATIC_CLUSTERING = OFF (when we add new data to the table it will not be automatically reclustered)
select * from CUSTOMER_CLONE where C_MKTSEGMENT = 'MACHINERY';
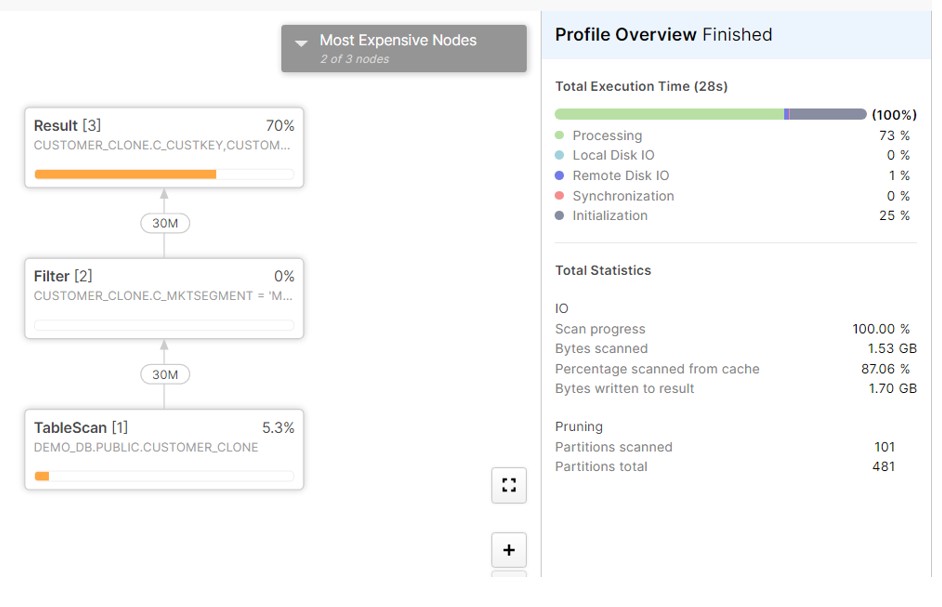
Now Insert the data into the CLONE table and observer the Query profile.
INSERT INTO CUSTOMER_CLONE SELECT * FROM CUSTOMER LIMIT 50000000;
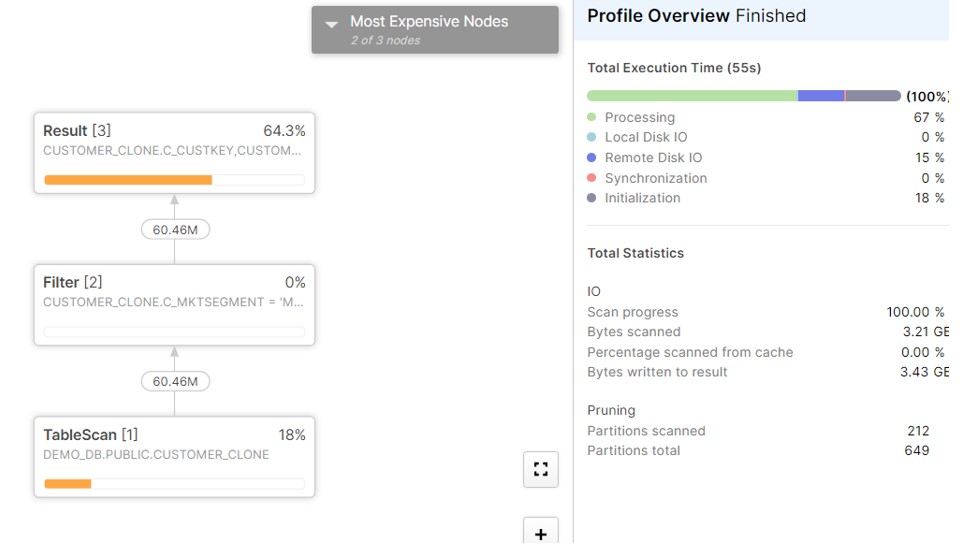
select * from CUSTOMER_CLONE where C_MKTSEGMENT = 'MACHINERY';
The query has read 212 partitions.
Now Resume the Cluster on table by using below command:
ALTER TABLE CUSTOMER_CLONE RESUME RECLUSTER;
SELECT * FROM TABLE(information_schema.AUTOMATIC_CLUSTERING_HISTORY());
select * from CUSTOMER_CLONE where C_MKTSEGMENT = 'MACHINERY';
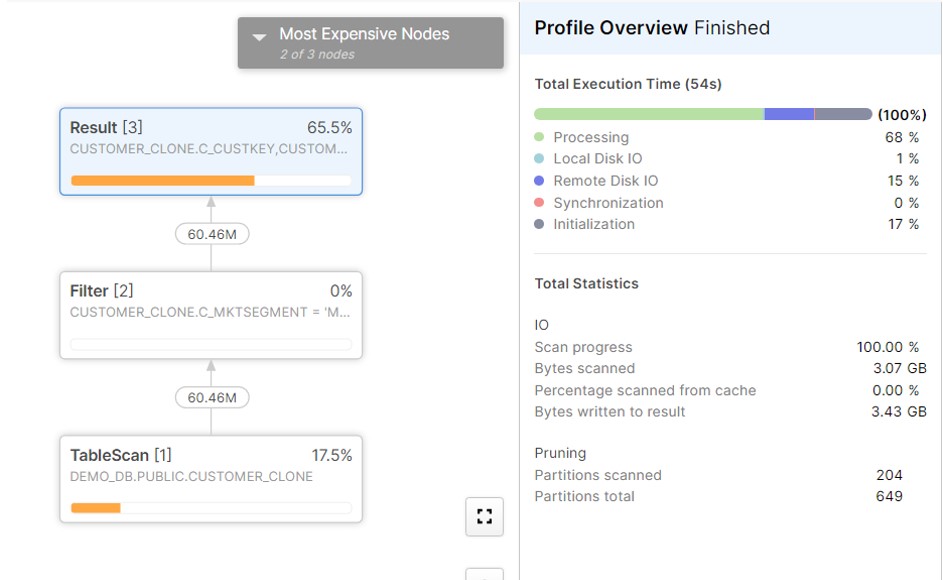
As we can see it has read 204 partitions after the Clustering. The same query took 212 partitions when Clustering was suspended on the table.
Case3:
Case3 : Create the new table using COPY command from an existing CLUSTERED table .We found Clustering did not create during the COPY operation.
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE CUSTOMER_COPY AS (SELECT * FROM CUSTOMER);
The copied table CUSTOMER_COPY is not clustered and AUTOMATIC_CLUSTERING = OFF, there is no clustering at all.
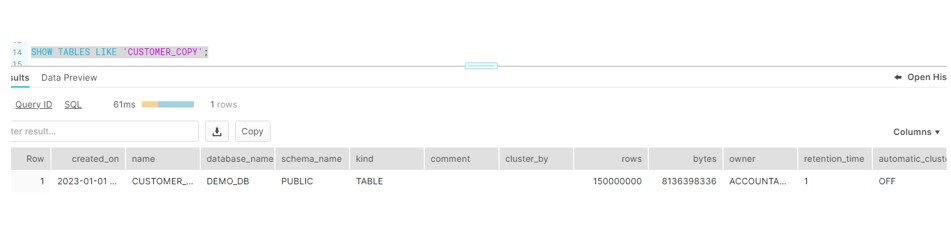
Now apply the clustering on COPY table.
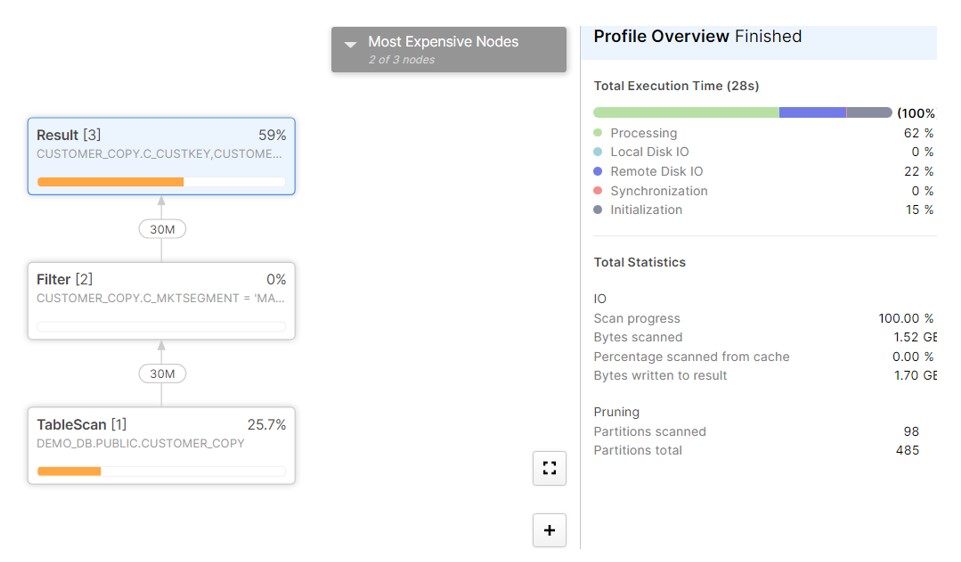
ALTER TABLE CUSTOMER_COPY CLUSTER BY (C_MKTSEGMENT);
Run the Query and check the Query profile and it has scanned only 98 partitions.
This way we could able to analyze the Cluster behavior on different table operations.