
The Challenge
Consider a typical enterprise scenario: your data team onboards new customer tables weekly, each containing various PII fields. Your compliance team requires all sensitive data to be properly tagged and masked based on user roles. Without automation, this becomes a bottleneck as data engineers manually identifying columns, applying tags, creating masking policies.
The Solution: Rule-Based Automated PII Governance
We’ve built a scalable, automated PII governance framework in Snowflake that transforms this manual process into rules-driven system. This solution demonstrates how to intelligently identify, tag, mask, and audit PII data with minimal human intervention.
Architecture Overview
Our solution consists of four key components:
- Configuration Layer
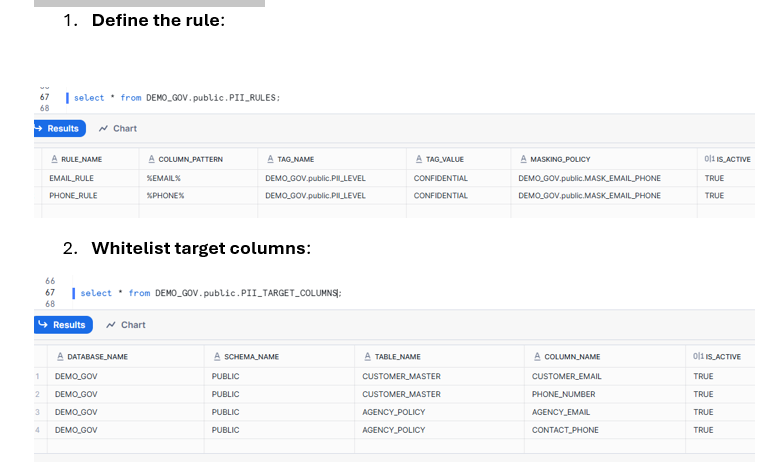
- PII_RULES: Central repository defining detection patterns, tags, and masking policies
- PII_TARGET_COLUMNS: Explicit whitelist of columns requiring governance (prevents over-tagging)
- PII_LEVEL Tag: Classification taxonomy (PUBLIC, INTERNAL, CONFIDENTIAL, RESTRICTED)
- Enforcement Layer
- MASK_EMAIL_PHONE: Dynamic masking policy showing real data only to privileged roles
- SP_AUTO_TAG_PII: Automated procedure applying governance rules at scale
- Audit Layer
- PII_DETECTION_AUDIT: Complete lineage of all governance actions with timestamps
- Testing Framework
- Role-based verification ensuring masking works as expected
What We Achieved
Automated Detection & Protection
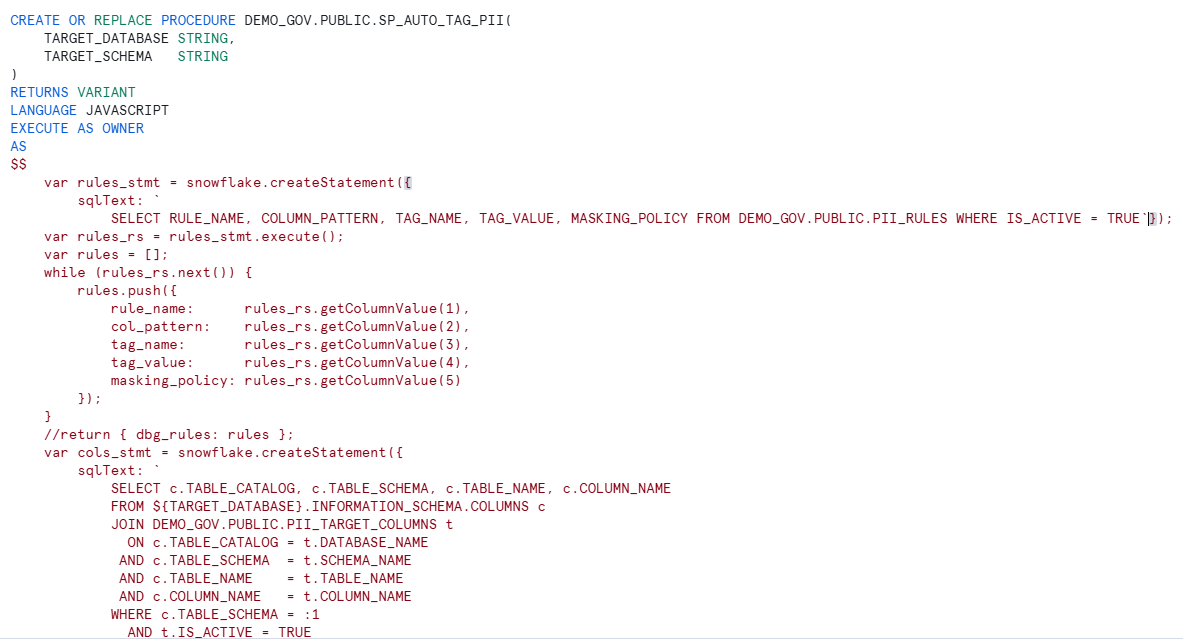
The stored procedure SP_AUTO_TAG_PII automatically:
- Scans designated columns against pattern-matching rules
- Applies classification tags (e.g., PII_LEVEL = ‘CONFIDENTIAL’)
- Enforces masking policies in a single execution
- Logs every action for compliance reporting
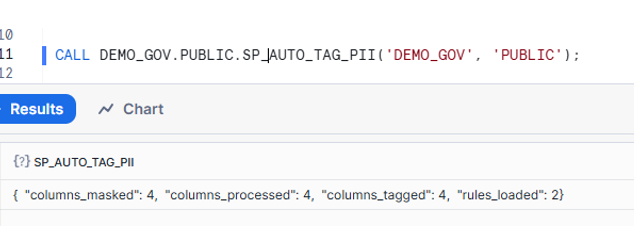
— One simple call protects your entire schema
CALL DEMO_GOV.PUBLIC.SP_AUTO_TAG_PII('DEMO_GOV', 'PUBLIC');
Result: In our demo, 4 PII columns across 2 tables were automatically tagged and masked in seconds—a process that would take hours manually.
Technical Implementation:
Technical Implementation:
3. Audit table
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE DEMO_GOV.public.PII_DETECTION_AUDIT (
RUN_TS TIMESTAMP_NTZ,
DATABASE_NAME STRING,
SCHEMA_NAME STRING,
TABLE_NAME STRING,
COLUMN_NAME STRING,
MATCHED_RULE STRING,
ACTION_TAKEN STRING,
ACTION_DETAILS STRING
);
4. Governance objects: Tag + Masking Policy
CREATE OR REPLACE TAG DEMO_GOV.PUBLIC.PII_LEVEL ALLOWED_VALUES 'PUBLIC','INTERNAL','CONFIDENTIAL','RESTRICTED';
CREATE OR REPLACE MASKING POLICY DEMO_GOV.PUBLIC.MASK_EMAIL_PHONE AS (val STRING)
RETURNS STRING ->
CASE
WHEN CURRENT_ROLE() IN ('ACCOUNTADMIN','SECURITYADMIN') THEN val
WHEN val IS NULL THEN NULL
ELSE '***MASKED***'
END;
5. Run the procedure:
CALL SP_AUTO_TAG_PII('DEMO_GOV', 'PUBLIC');


No code changes required—the framework adapts to new requirements through configuration.
Stored Procedure Logic Flow
Stored Procedure Logic Flow
a): Load Active Governance Rules
- Queries PII_RULES table to fetch all active rules (IS_ACTIVE = TRUE)
- Each rule contains:
- Pattern to match (e.g., %EMAIL%, %PHONE%)
- Tag to apply (e.g., PII_LEVEL = ‘CONFIDENTIAL’)
- Masking policy to enforce (e.g., MASK_EMAIL_PHONE)
- Stores rules in a JavaScript array for processing
b): Identify Target Columns (Whitelist Approach)
- Joins INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS with PII_TARGET_COLUMNS
- Only processes explicitly whitelisted columns
- Filters by target database and schema passed as parameters
c): Pattern Matching & Rule Application
- Loops through each whitelisted column
- Matches column name against rule patterns (case-insensitive)
- For each match:
- Applies classification tag using dynamic ALTER TABLE statement
- Enforces masking policy using dynamic SQL
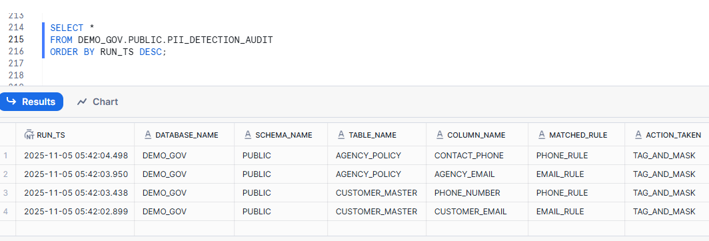
d): Audit Trail Logging
- Records every governance action in PII_DETECTION_AUDIT table.
6. Verify Audit Log Table.
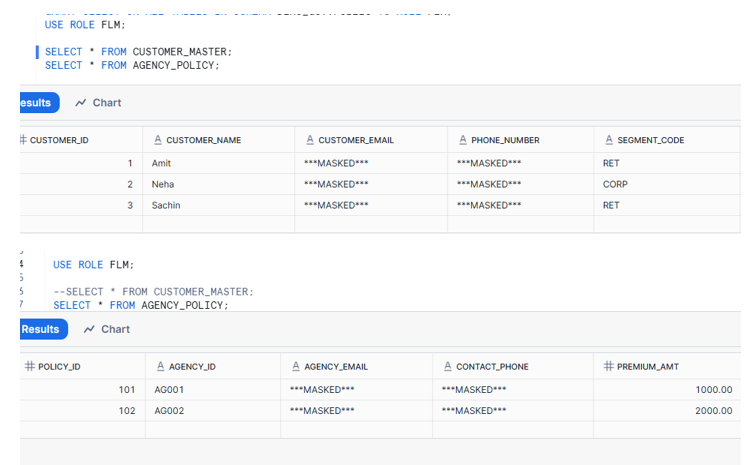
Role-Based Access Control
The masking policy implements intelligent role-based data access:
- ACCOUNTADMIN/SECURITYADMIN: See actual data (amit@example.com, 9999999999)
- Standard roles (FLM): See masked values (***MASKED***)
Conclusion
This framework demonstrates that with thoughtful architecture, you can:
- Protect sensitive data without slowing down data teams
- Scale governance across hundreds of tables and schemas
- Maintain complete auditability for regulatory requirements







